Active Engine
Overview
The active engine function allows users to control the number of AI tasks running in parallel. This feature helps prevent CPU/GPU overload by limiting simultaneous processing and introducing controlled idle periods
Feature Purpose
- Limit simultaneous AI tasks to avoid resource overconsumption.
- Introduce controlled idle periods for resource recovery.
- Optimize overall system stability when tasks do not need constant execution.
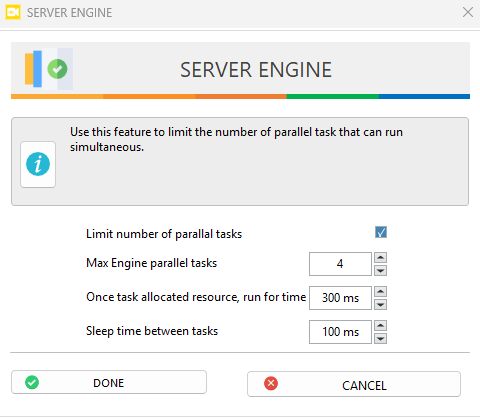
Settings
Turn the feature on or off by using the limit number of parallel task checkbox. When disabled, tasks run without restrictions.
Max Engine Parallel Tasks: Sets the maximum number of tasks that can run at the same time.
Run For Time: Defines how long (milliseconds) the current set of parallel tasks will run before stopping to allow other set of tasks to execute. (0ms = tasks run for 1 frame)
Sleep Time Between Tasks: Specifies how long (milliseconds) the system remains idle before starting the next set of parallel tasks, allowing resource recovery, improving system performance
Max Engine Parallel Tasks: 4
Run Time per Task Set: 300 ms
Sleep Time Between Task Sets: 100 ms
Result: 4 tasks run simultaneously for 300 ms, then system idles for 100 ms before starting the next set.
Adjust the above parameters based on system load and performance needs as:
- Setting X parallel tasks ensures resource usage is limited to X tasks at a time, rather than the total number of queued tasks.
- Lower Max Parallel Tasks → Smaller batches, resulting in more waiting time for queued tasks due to run time and sleep time constraints.
- Higher Run Time → Tasks run longer, but queued tasks will wait more before execution.
- Lower Run Time → Tasks run for a shorter duration, enabling faster rotation between task sets.
- Sleep Time = 0 → The next set of parallel tasks starts immediately without releasing resources.
- Higher Sleep Time → Longer idle periods, delaying next task set but allowing better resource recovery.